COMAP cryostat interior
Interior of COMAP cryostat showing 19 low noise amplifiers.
COMAP cryostat exterior
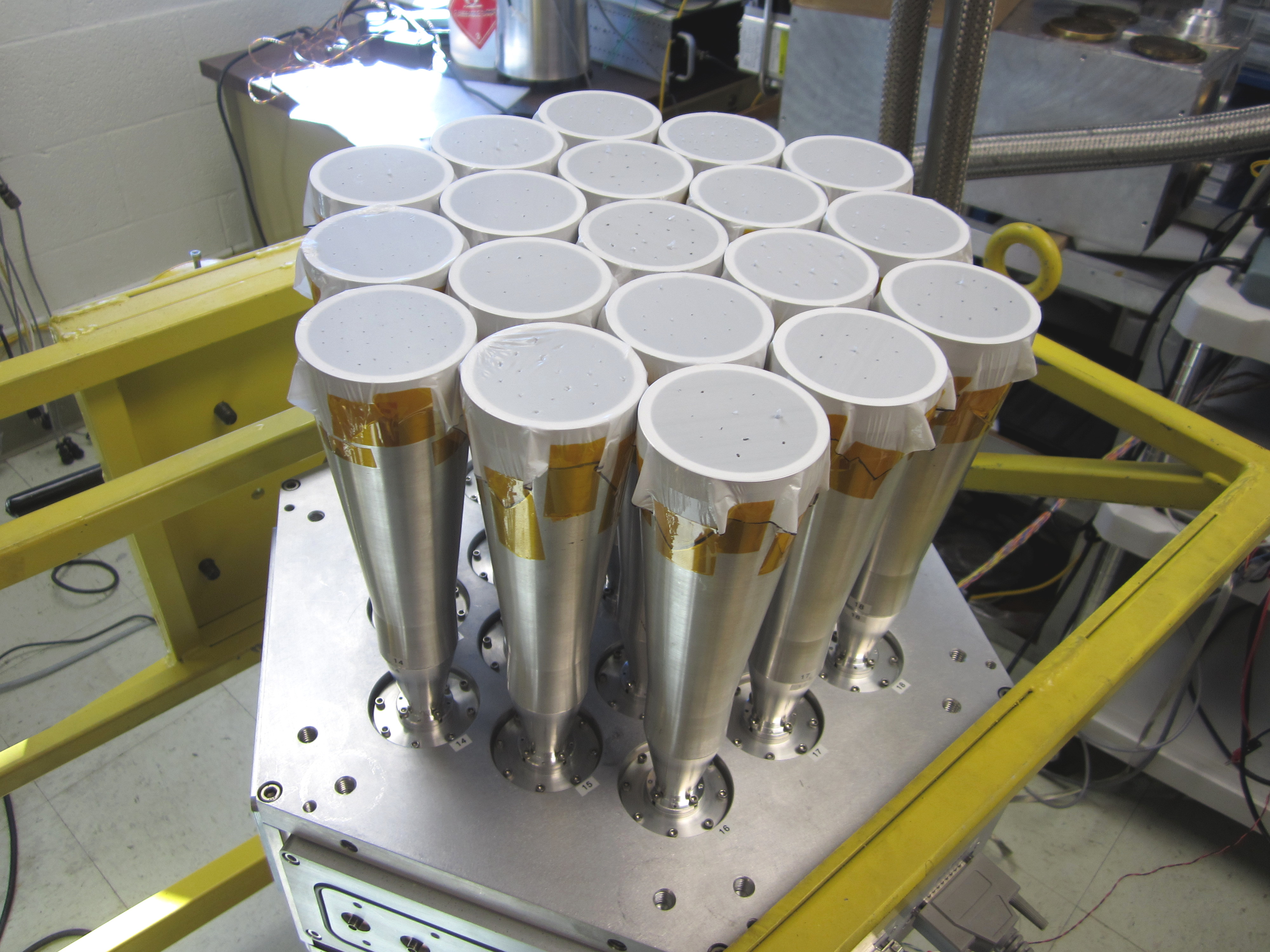

COMAP cryostat exterior showing 19 ambient-temperature feed horns.
Argus receiver
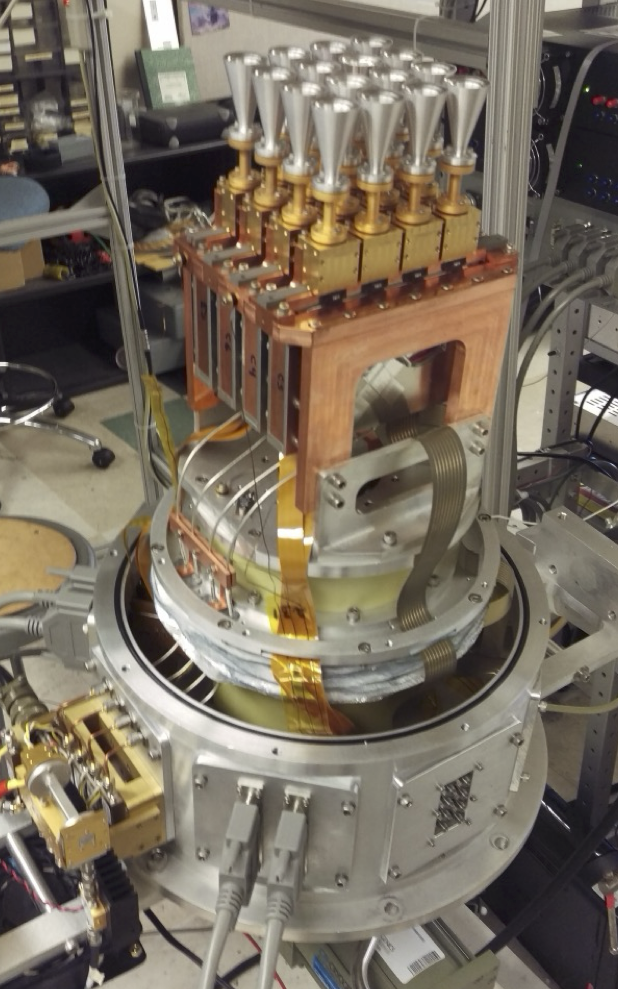
Argus receiver, showing miniaturized receiver modules designed and fabricated at CRAL
QUIET W-band polarimeters
91 W-band polarimeter modules
Building the Next Generation of Instruments
By incorporating our improved detectors into miniaturized receivers for focal plane arrays, we are building radio cameras that push the frontiers of radio astronomy. The measurement of faint signals over large angular scales, requires the packing of many (individually very sensitive) receiver elements close together, to make a radio camera. This requires advances in detector performance but also in miniaturization of receiver electronics and routing of signals. The CRAL has built significant expertise in this area through the development of radio cameras for COMAP (line intensity mapping), Argus (wide-area, low surface-brightness mapping) and QUIET (CMB polarization).
30 GHz Low noise amplifier modules for the CO Mapping Array Project (COMAP)
The COMAP Pathfinder uses a 19-feed spectrometer array operating at 26-34 GHz. The 19 LNA modules, each containing two MMIC LNA chips, were produced at the CRAL. The cryogenically cooled modules form the front end for the Pathfinder receiver and are the critical component in determining the instrument’s sensitivity. The Pathfinder is performing a spectral line intensity mapping survey of carbon monoxide at z=2.4-3.4. Based on observations to-date, the project has imposed the first constraints on the CO(1-0) power spectrum on clustering scales. Observations are ongoing, with the aim to make the first detection of the CO power spectrum.
Kieran A. Cleary, and the COMAP Collaboration, COMAP Early Science. I. Overview, The Astrophysical Journal, vol. 933, no. 2, article 182, July 2022. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac63cc
James W. Lamb, Kieran A. Cleary, and the COMAP Collaboration, COMAP Early Science. II. Pathfinder Instrument, The Astrophysical Journal, vol. 933, no. 2, article 183, July 2022. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac63c6
100 GHz receiver modules for Argus
Argus is a 16-feed 100 GHz spectrometer array operating on the Green Bank Telescope. At the CRAL, we produced the miniaturized receiver modules, as well as the IF electronics. The receiver modules incorporate two MMIC low noise amplifiers of a JPL design, and a Schottky diode IQ mixer, with an external LO source. These miniaturized modules allowed close-packing of the 16 feeds forming this focal plane array spectrometer. The MMIC amplifiers were cryogenically probed prior to module assembly. This allowed pre-selection of the devices with the best cryogenic performance.
R. Gawande, R. Reeves, K. Cleary, et al., W-band heterodyne receiver module with 27 K noise temperature, in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, article 6259612, June 2012. doi:10.1109/MWSYM.2012.6259612
90 GHz polarimeter modules for the Q/U Imaging ExperimenT (QUIET)
QUIET used an array of 91 miniaturized polarimeters operating at 100 GHz, each containing 6 MMIC LNAs, two phase switches, a phase discriminator and direct detection diodes. These were subsequently redesigned at the CRAL to improve noise temperature and linearity. The QUIET instrument aimed to measure the B-mode polarization of the cosmic microwave background. It was fielded on the Chajnantor Plateau in the Chilean Andes.
Kieran A. Cleary, Coherent polarimeter modules for the QUIET experiment, in Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy V, eds. Wayne S. Holland and Jonas Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE 7741, 77412H (July 2010). doi:10.1117/12.857673
